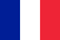
Psoriasis (translated from Greek "psora" - "skin disease, scabs") is a chronic pathology of non-infectious nature, also known as scaly lichen, which mainly affects the skin of the knee and elbow joints, lower back and head. There is also psoriasis of the joints, bones, nails, external genitalia and internal organs, but these forms are rarely diagnosed. The pathology is difficult to cure, therefore, when the first symptoms appear, red rashes, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Symptoms
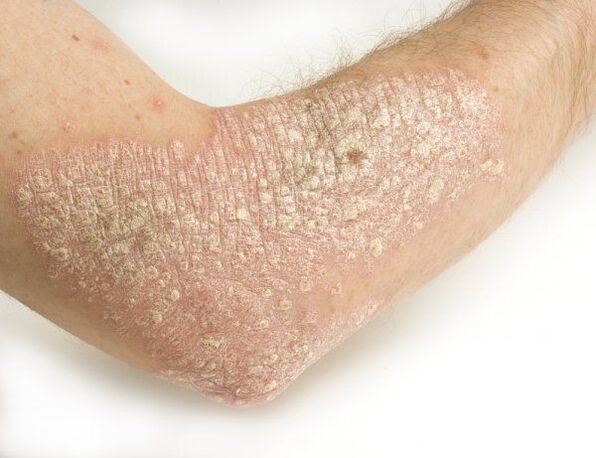
Stearin stain
The first sign of psoriasis, which is part of the triad of symptoms of the pathology. It is characterized by increased peeling after scraping the affected surface with a spatula. Over time, there is a separation from the papules of silvery-white scales. They are not difficult to remove as they become loose and poorly adhere to the psoriatic papule. The surface of the neoplasms (rash) turns white and the particles crumble and look like sawdust.
The first phenomenon of the triad is explained by the development of parakeratosis (malfunction of the epithelium, which leads to a violation of the formation of the stratum corneum). Local non-hormonal agents (creams, ointments) are used to combat the deviations in the initial stage.
Terminal film
It is characterized by the removal of a thin layer of tissue from the papules, which has a shiny structure and resembles polyethylene. It is easily separated from any impact (pressure, friction, etc. ) after removal of dried scales.
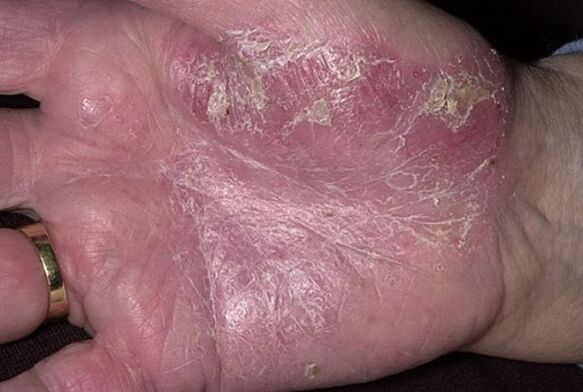
The final film is the last layer that is removed from the skin. Further scraping leads to the last stage of the triad - drip bleeding.
At this stage, medicinal herbal baths, drugs with anti-allergic effect, natural-based ointments (without corticosteroids and hormones) are used.
Accurate bleeding
After removal of the final film, drip bleeding occurs on the affected area of skin (symptom of auspitis or "bloody dew") and there is an accelerated growth of tumors, which sometimes reach the size of a pea and are called lenticular. diameter of a small coin and differentiate as nummular. With the progression of the disease their growth increases and when combined, psoriatic plaques are formed.
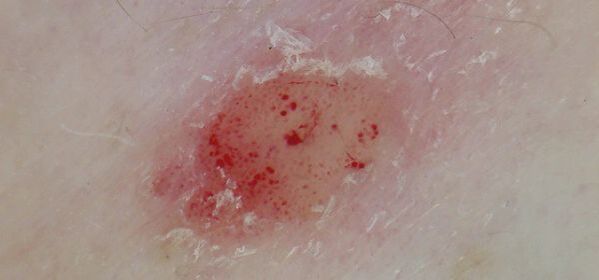
Retinoids, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy are used for treatment.
Others
The disease can be recognized by other characteristic signs, the main of which are 4:
- The rim is red, not covered with scales, which forms around the papules.
- Small rashes are visible on a clean area of skin (usually appearing before the progressive stage of psoriasis).
- A symptom that helps to distinguish psoriasis from seborrheic dermatitis is characteristic of the active stage of the pathology. It is accompanied by the appearance of papules with clear borders on the scalp; this does not happen with seborrheic dermatitis.
- A light, shiny edge of skin appears around the formation. The symptom is typical of a stage of disease regression and occurs when the papules disappear.
How it looks
In most cases, the onset of the pathology is unnoticeable: at an early stage, psoriasis affects small areas of the skin, mainly in the curves of the limbs, head and hairline.
Attention!The initial manifestations appear at the site of constant mechanical skin irritation, for example where clothes are rubbed and pressed.
Common symptoms:
- itching;
- excessive dryness of the skin;
- peeling of pathological elements;
- general deterioration of health (weakness, lethargy, fever).
There are 3 stages of development of pathological papules:
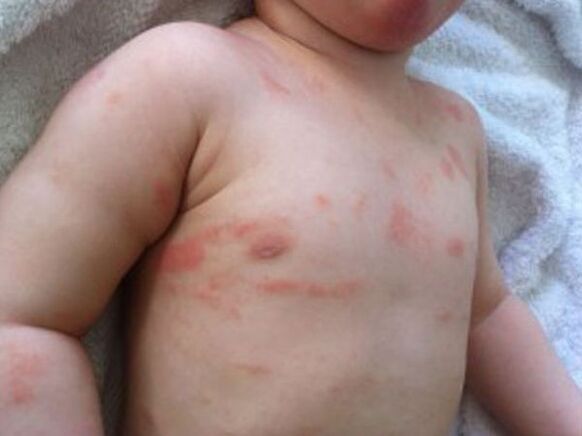
- Progressive.The appearance of a rash with a bright pink tinge, surrounded by a rich, slightly indistinct edge. In the center of the papules, the skin peels off, giving the formations a white color. At this stage, the rash may appear at the site of scratches, skin injuries, bites, cuts, punctures or burns.
- Stationary.It starts 1-4 weeks after the onset of the disease. New plaques do not appear, the old ones acquire a light color, the intensity of peeling decreases.
- Regressively.The color of the plaques and papules fades, their infiltration decreases and the formations dissolve. The average duration of the rotting period is from 2 to 6-8 months.
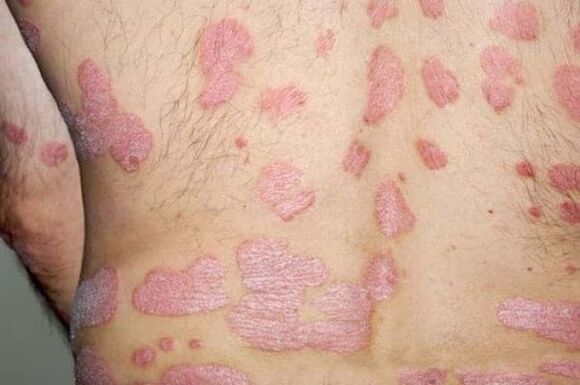
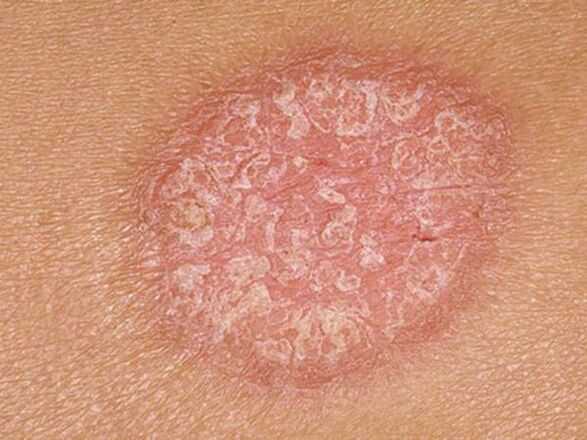
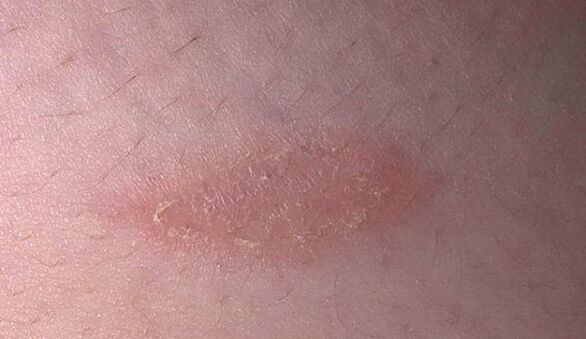
Symptoms of the disease depending on the species:
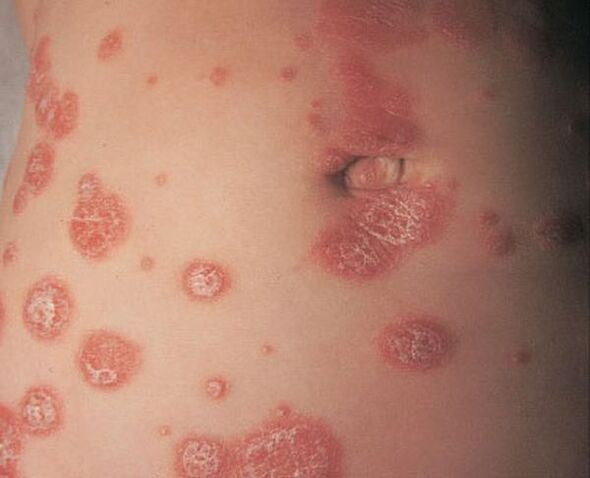
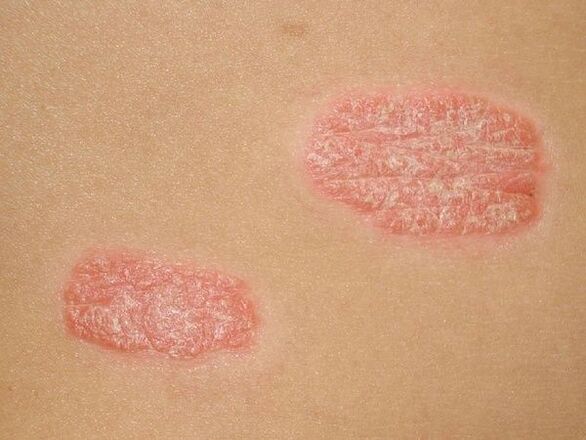
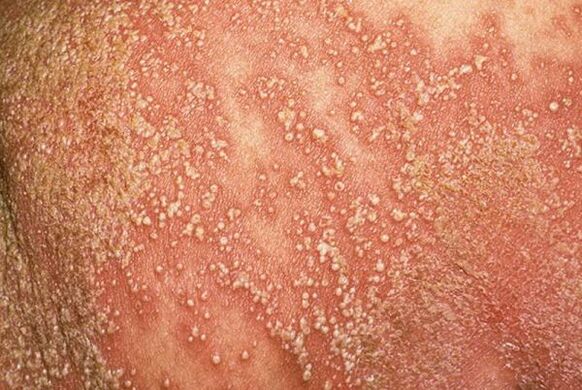
- She cried(common or vulgar). The most common type of pathology. Oval or round plaques with a red tinge, covered with silvery-white scales on top, appear on various parts of the body (more often on the elbows, knees, head).
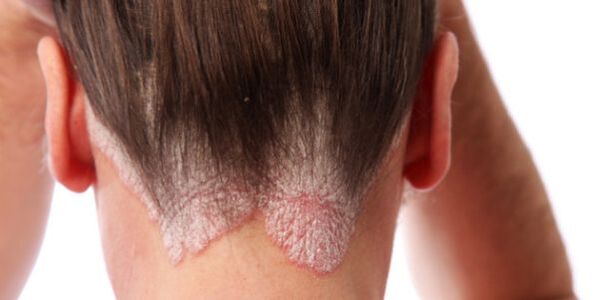
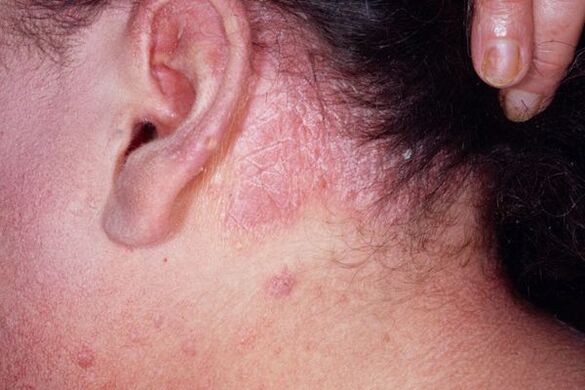
- Seborrheic.It appears mainly on the scalp. Manifested as peeling and itching, spreads to the area behind the ears and skin along the hairline.
- Pustularthe species is considered the most severe form, develops rapidly and affects large areas of skin. Painful rashes appear on the body, which are accompanied by a local increase in temperature, weakness, headache, diarrhea. Soon, vesicles filled with exudate form in the lesions. In the future, the spots progress, merge with each other, forming large lesions on the body.
- Intertriginous.Typically for children, accompanied by the appearance of bright red papules, with a slight peeling (may not be there).
- Exudative.The affected areas of the skin not only peel off, but also get wet, yellowish crusts form on the surface of the plaques.
- Psoriatic erythroderma.Red plaques with silvery, yellow or white scales are observed throughout the body. It is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, fever. In the future, the formations merge into large spots that cause irritation and itching.
- Psoriatic arthritis.It is accompanied by a "joint syndrome" in which the skin in the area of the joints (wrists, phalanges of the fingers, spine, etc. ) is affected and if measures are not taken in a timely manner, the disease affects the joints.
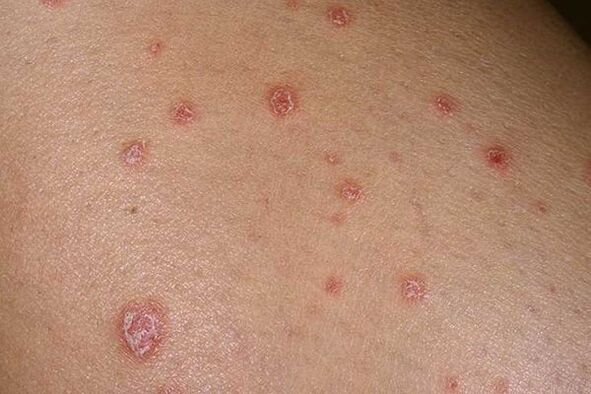
- A tear dropaccompanied by abundant rashes consisting of numerous small plaques. In this case, the papules are in the form of drops, their color is from bright red to purple.
- Point.It is characterized by the formation of small spots on various areas of the body resembling dots, and there may be no scaling of the dermis.
- Rupioid.One of the types of chronic psoriasis. Crusts appear on the formations, they become taller, taking the shape of a cone.
- Starmanifests itself in large papules that do not last long, sometimes papillomas and warts form on them.
- Psoriatic onychialeads to deformation of the nails, the appearance of yellow-brown spots under them.
- Palmar-plantar.Appears on the palms and soles. The main symptoms are thickening of the skin, dryness, cracks.
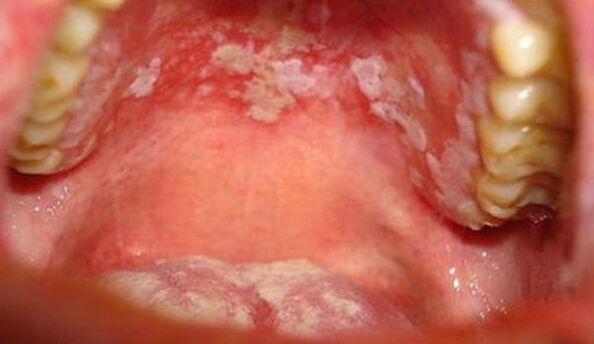
- Mucosal psoriasisaffects the oral cavity and provokes the appearance of plaques on the mucosa.
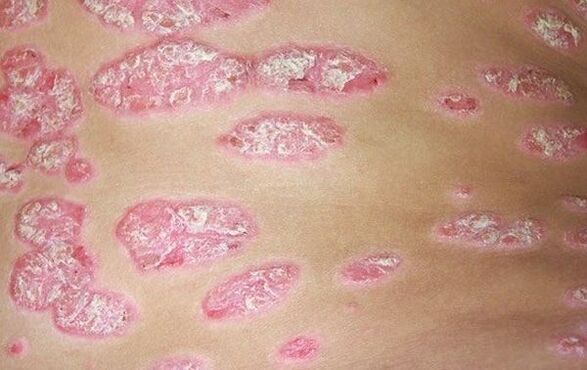
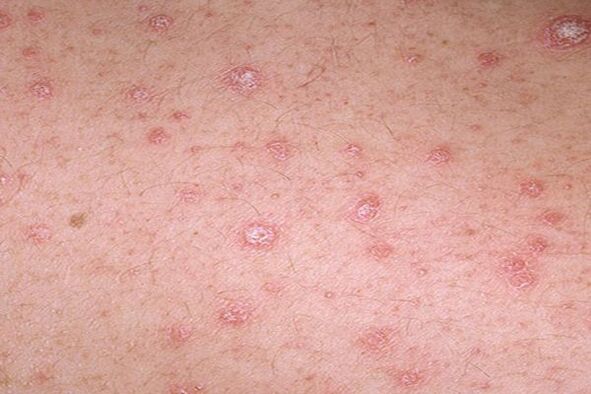
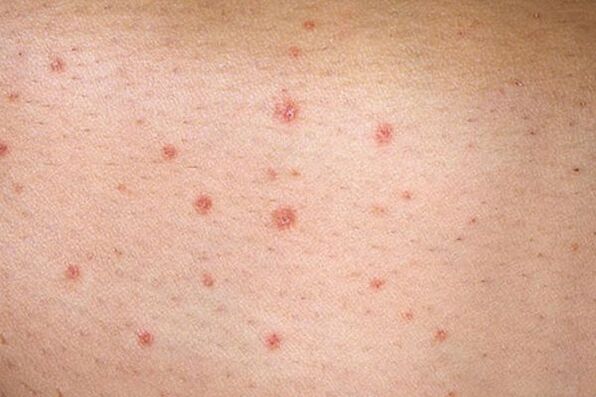
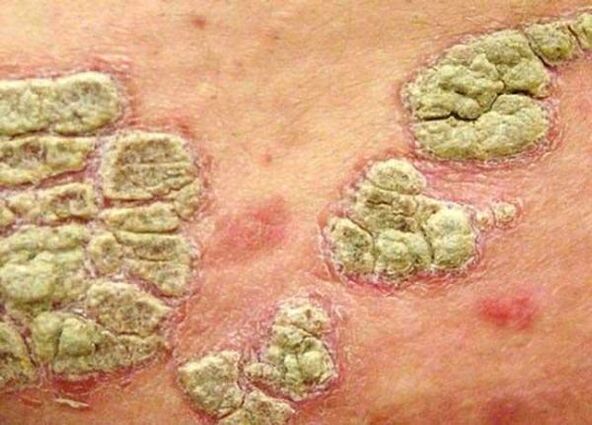
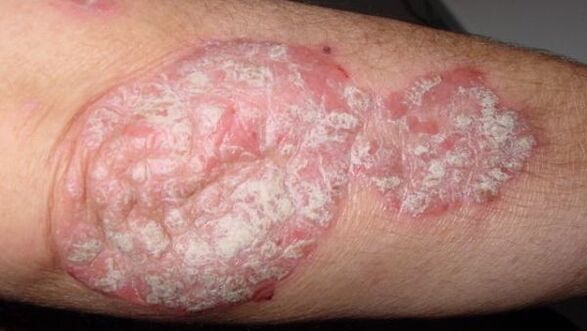

Localization of psoriasis
Hands
In most cases, the rash appears on the surface of the elbows or between the toes. Papules of the forearm are less common.
Attention!The hands are characterized by a plaque form of pathology, but there are others. Its sign are small spots of red tint, quickly covered with white scales, the affected skin rough.
Legs
Psoriatic lesions occur mainly on the legs in the knee area, but may also occur on other parts of the legs.
The first rash is single and small with clear outlines, but loose, inflamed and strongly scaly. These precise papules spread rapidly, forming conglomerates.
Chapter
It often develops against the background of seborrhea, affects the hairline, forming the so-called psoriatic crown. Skin formations gradually grow and spread over the entire surface, resembling dandruff. This localization occurs quite often, less often there is a rash on the ears or behind them.
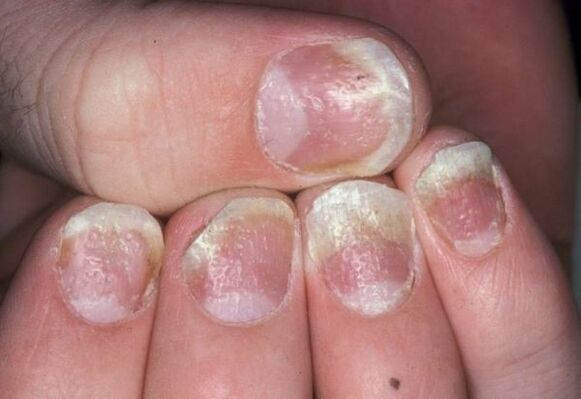
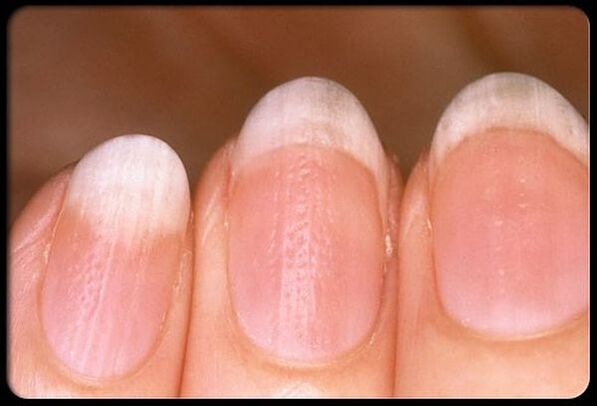
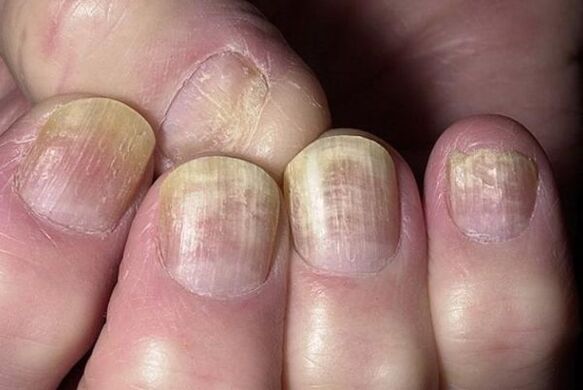
Fingernails
The nail plate can be affected by the type:
- Thimble- point form of psoriasis. Small pits appear on the nails, which look like a needle prick.
- Onychomycosis- The nail changes color, becomes dull, noticeably thickens and begins to peel. A psoriatic papule can be seen through the plaque, surrounded by a reddish edge, like an oil slick.
Body
It usually manifests as characteristic papules that merge with each other. Psoriasis is more common on the back, less often on the neck, abdomen, hips, the formations may be drop-shaped, punctate and plaque.
Face
Rarely affected, the rash is found in the nasolabial folds, in the temples and eyebrows, around the eyes. Rarely, the pathology affects the border of the lips, the rash resembles herpes.
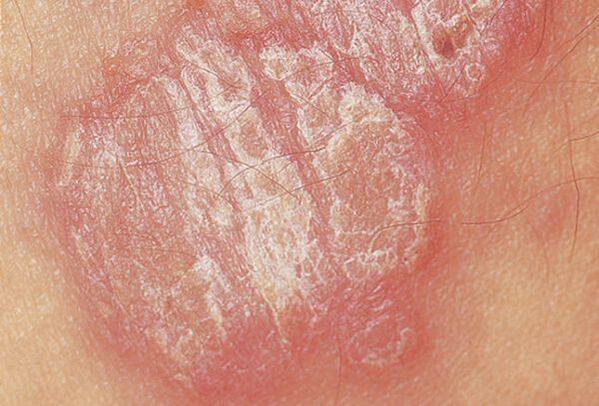
Palms and feet
Both areas are affected simultaneously, but there are cases when the pathology develops only on the feet or palms. On the soles, the disease is often combined with fungal pathology, which significantly complicates the diagnosis and therapy.
This type of psoriasis is divided into 3 types:
- Papular plaque- the formations are dense, do not protrude above the skin, it is difficult to separate the scales from the plaque. The rash appears in the border areas, accompanied by swelling and keratosis.
- Psoriatic callus- round dense papules consisting of keratinized epidermis. The skin layer gradually thickens and thickens. As a result, it is easily injured, cracks appear. There is practically no redness, the size of the growths is from 2-3 millimeters to 2-3 centimeters.
- Vesicular-pustular- manifests itself in the form of serous-purulent papules. The bubbles reach 2 millimeters in diameter and tend to coalesce.
Compounds
The pathology can affect a person's joints, leading to a change in the structure of their tissues, which progressively leads to pain and deformity. External symptoms: a reddish rash appears on the skin. Internal signs - joint pain, especially during sleep, stiffness of movements, swelling.
Important!First, psoriasis affects the small joints of the legs and arms, then spreads to the knee and elbow, and at an advanced stage the intervertebral joints already suffer.
Itching or not
In most cases, psoriatic disease is accompanied by itching of varying intensity, sometimes not only spots, but also the whole body itches. In the initial stage, the itching is mild, gradually increasing.
The degree of intensity also depends on the location of the pathology. For example, psoriasis on the scalp itches a lot, while the skin whitens and falls into large scales larger than normal dandruff in size. In the stationary stage, the itching decreases, often giving way to a burning sensation. During remission, all major symptoms are mild.
Itching worsens with:
- relapse;
- climate change;
- general intoxication;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- joining scabies, allergies;
- HIV infections.
The skin itches severely after drinking coffee, alcoholic beverages, spicy and spicy foods, chocolate and other allergens.
How to distinguish
In eczema
- The nature of the rash.In eczema, the blisters or blisters fill with fluid that periodically leaks out. Psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of dry scaly papules, when blood appears.
- Itchy skin.From eczema the body itches more than in psoriatic pathology.
- Color.In psoriasis, the scales have a silvery tinge, and in eczema the affected areas become bright red or scarlet.
- Sick areas.Eczema affects the soft, sensitive areas of the skin, armpits and groin. Psoriasis is characterized by a rash on rough, hard and thick layers of skin (knees, elbows, head and others).
- The causes of the disease.Psoriasis is often caused by neurogenic factors, and eczema is caused by allergies and malfunctions.
- Characteristics of rashes on the hands.With nail plate psoriasis, pits form and eczema is similar to a fungal infection.
For seborrheic dermatitis
The clinical manifestations of the diseases are similar, but there are several characteristics by which you can distinguish them:
- psoriasis is characterized by unhealthy glow of the skin and bloody cracks, and this is not observed in seborrheic dermatitis;
- dermatitis, unlike psoriasis, is not accompanied by roughening of the skin and its severe dryness;
- in psoriasis the scales are silvery and the seborrhea is yellow or white;
- seborrheic scales are easily removed, but psoriatic ones are not;
- dermatitis is more common in areas of accumulation of sebaceous glands, and scaly diseases - throughout the body;
- scalp psoriasis noticeably goes beyond the area of hair growth and seborrheic pathology does not exceed this limit;
- the area of lesion with flat lichen is much larger than that of dermatitis.
From fungi
- Psoriasis occurs in the presence of several provoking factors, such as heredity, mechanical damage to the skin, malfunction of the immune system, etc. The cause of the second disease are only the spores of parasitic fungi.
- Psoriatic pathology is not contagious, it is not transmitted by air, sexually or by touch.
Attention!The fungus (onychomycosis) affects all contact, including in public places - sauna, swimming pool, gyms, etc. It is transmitted by animals and humans.
- In scalp psoriasis, the structure of the hair does not change, while fungal diseases lead to brittleness, dryness and hair loss.
- Unlike scaly lichens, onychomycosis of the feet and legs is accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
- With the defeat of scaly nails, their structure changes at the initial stage, and with fungi for a long time the structure and color of the nail plates do not change.
From pink herpes
The hallmark of psoriasis is the "psoriatic triad". The disease grows gradually and goes through 3 stages. Pityriasis rosea (pityriasis) develops rapidly and progresses. In addition, pityriasis is a contagious disease, but scaly lichen is not.
From neurodermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis) is of allergic origin and is triggered by a specific substance, such as plant pollen, food, animal hair, etc. The causes of psoriasis are different (heredity, reduced immunity, psychosomatics, mechanical damage to the skin, etc. . ).
- In neurodermatitis the skin dries out and becomes rough, and in psoriasis it flakes and bleeds.
- Plaques with dermatitis consist of individual small elements, in the case of shingles, the papules are homogeneous and covered with silvery scales.
- The color of the rash in psoriasis is much brighter than in neurodermatitis.
For gout
The difference between gouty and psoriatic arthritis lies in the cause of the development. Gout occurs when uric acid crystals are deposited in the cartilage of the joints. Deviation from the norm can be provoked by: arterial hypertension, obesity, taking diuretics, drinking alcohol, etc.
The symptoms of psoriasis and gout are similar - severe pain at night, stiffness on the move, redness and swelling in the affected area. In psoriasis, however, in most cases, characteristic red rashes appear first, followed by pain.
Other distinguishing symptoms of gouty arthritis include:
- the presence of white nodules in the affected joint;
- signs of kidney stones (back pain, blood in the urine, etc. ).